Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of technological progress, transforming industries from healthcare to entertainment. Behind the sophisticated algorithms and cutting-edge applications lies a critical but often overlooked role—the AI Trainer. These professionals ensure AI models are not only accurate but also adaptable and fair, acting as the bridge between theoretical algorithms and practical, human-centric applications.
As AI continues to permeate our lives, the importance of AI Trainers grows exponentially. They shape AI's ability to learn, adapt, and solve real-world problems, making them indispensable in the AI ecosystem. Whether you're a data scientist, a business leader, or an AI enthusiast, understanding the role of AI Trainers is crucial for navigating the future of AI innovation.
1. What is an AI Trainer?
AI Trainers are the unsung heroes behind every effective AI system. They prepare the raw data that feeds AI models, ensure the algorithms are tuned to perfection, and troubleshoot issues that arise during training. Within this scope, AI Editors play a more specialized role, focusing on refining and validating AI-generated outputs. They ensure clarity, accuracy, and adherence to ethical and linguistic standards, bridging the gap between raw AI responses and polished, real-world results.
This article will explore both roles in detail, shedding light on their unique contributions, skill requirements, and growing importance in the AI industry.
2. Essential Skills for AI Trainers
The dual nature of this role—requiring both technical and interpersonal skills—sets AI Trainers apart.
Technical Skills
An AI Trainer’s technical toolkit includes expertise in:
- Data Analysis: Proficiency in cleaning, augmenting, and organizing data using Python libraries like pandas or tools like Tableau.
- Algorithm Tuning: Familiarity with optimization techniques, such as hyperparameter tuning.
- Specialized Tools: Experience with AI frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or advanced methods such as transfer learning.
Soft Skills
Soft skills can make or break an AI Trainer’s success. For instance:
- Communication: Translating why a model underperformed due to biased training data for non-technical stakeholders requires clarity and tact.
- Problem-Solving: Addressing anomalies, such as corrupted datasets or overfitting issues, demands creative thinking.
3. Training Techniques and Methodologies
AI Trainers employ various methodologies depending on the task and its complexity. Below is a comparison of commonly used approaches.
| Training Technique | Description | Best Use Cases | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Models trained on labeled datasets | Classification (e.g., spam detection), regression tasks | Requires large labeled datasets |
| Unsupervised Learning | AI discovers patterns in unlabeled data | Market segmentation, recommendation systems | Challenging to validate outputs |
| Reinforcement Learning | Models learn via rewards and penalties | Game AI, autonomous vehicles | Computationally expensive |
| Semi-Supervised Learning | Mixes labeled and unlabeled data | Scenarios with limited labeled data, e.g., customer segmentation | Moderate accuracy improvement |
| Transfer Learning | Leverages pre-trained models for new tasks | NLP, image classification | May require domain-specific adjustments |
4. The AI Editor: A Key Role in Shaping Human-Centric AI
As AI systems become more integrated into daily life, ensuring their outputs are human-readable, accurate, and engaging has become a critical task. This responsibility falls on AI Editors, professionals who bridge the gap between AI's raw outputs and polished, user-ready content.
Differences Between AI Trainer and AI Editor
| Aspect | AI Trainer | AI Editor |
|---|---|---|
| Core Role | Focuses on preparing datasets, training AI models, and improving algorithms | Polishes and refines AI-generated outputs and human-written texts for human consumption |
| Responsibilities | Data categorization, model tuning, bias detection, and retraining | Grammar correction, tone adjustment, and consistency checks |
| Skills Required | Machine learning expertise, data analysis, and familiarity with AI frameworks | Linguistic mastery, editing expertise, and attention to detail |
| Focus | Developing and improving AI systems | Ensuring output meets human standards of quality |
| Tools | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Jupyter Notebooks | Editing platforms, content management tools |
| Outcome | Optimized and functional AI systems | Readable, accurate, and engaging AI outputs |
The AI Editor Role in Our Company: Comprehensive Overview
In our company AI Editors handle writing-intensive tasks and focus on producing polished outputs suitable for real-world applications. Here's a detailed look into what the position entails, the challenges it presents, and the opportunities it offers.
Responsibilities of AI Editors
AI Editors in our company play a crucial role in ensuring AI systems meet quality benchmarks. Their key duties include:
- Writing and Editing Specialized AI-Related Texts
Create and refine specialized content to train and enhance AI models.
- Researching and Exploring Relevant Topics
Study various subject areas to enrich AI models with accurate and diverse information.
- Fact-Checking and Verifying Information
Search for credible sources to ensure all content and facts used are trustworthy.
- Evaluating and Ranking AI-Generated Responses
Assess the quality of AI model outputs, providing rankings based on accuracy, relevance, and clarity.
- Ensuring Compliance with Language Rules
Check AI-generated texts for grammatical accuracy, proper structure, and adherence to the rules of the language.
- Improving AI-Generated Texts
Edit and enhance neural network-generated content to improve its style, logic, and quality.
Summarizing Text Content
Write concise and clear summaries of longer texts to simplify the information for AI training and outputs.
- Writing Logs for Model Training:
Draft and refine question-answer pairs that train models to handle similar queries effectively.
- Classifying Specialized Tasks:
Work on specific classification projects while keeping them separate from editing tasks to prevent cognitive fatigue.
- Creating Suggestions for AI Applications:
Generate predictive suggestions for chatbots (similar to advanced T9 functionalities) to improve user interactions.
Develop recommendation prompts for client projects like music or content suggestions.
Examples of Work and Case Applications
- Music Recommendations:
AI Editors create and validate recommendation datasets for personalized music playlists.
- Chatbot Suggestions:
Crafting context-based predictive phrases to enhance chatbot accuracy and conversational flow.
Challenges in the Role
While the position of AI Editor offers unique opportunities, it also comes with notable challenges:
- Dynamic Work Environment:
Clients often struggle to define their needs due to the novelty of the field, requiring editors to adapt quickly.
- Constant Updates:
Technical specifications (TS) often change 2–3 times weekly, demanding continuous learning and flexibility.
- Critical Thinking:
Evaluating assessors’ annotations or AI-generated content requires strong analytical skills and logical reasoning.
- Monotony:
Some tasks, like repetitive text validation, require patience and focus.
Why Choose This Role?
The AI Editor role is ideal for individuals who enjoy working at the intersection of language and technology. Here’s what makes this profession appealing:
- Impactful Work:
Directly contribute to AI systems that shape future technologies and improve user experiences.
- Remote Work Flexibility:
Editors can work remotely, with the freedom to manage their schedules as long as targets are met.
- Dynamic Topics:
Exposure to a variety of projects, from music recommendations to conversational AI, keeps the work interesting.
Who Thrives in This Role?
This role is suited for individuals with the following qualities:
- Educational Background:
- Preferred candidates include linguists, philologists, journalists, and copywriters.
- Key Skills and Traits:
- Patience and persistence for handling repetitive or evolving tasks.
- Curiosity and adaptability to dive into diverse projects.
- Attention to detail and analytical thinking for evaluating errors and ensuring text quality.
- Strong critical thinking skills to assess outputs and justify decisions effectively.
Career Growth Opportunities

Our company offers a structured pathway for career progression:
- Starting as an Assessor:
Candidates often begin with annotation tasks, learning the foundations of data preparation before advancing to editing roles.
- Becoming an AI Trainer:
Editors with extensive experience may transition to AI Trainer roles, where they prepare and refine datasets directly used in training machine learning models.
Working Conditions for an AI Editor
The role of an AI Editor offers a balance of structured responsibilities and flexible work conditions tailored to ensure efficiency and focus.
- Collaborative Environment
AI Editors work closely with team members, engaging in regular discussions to stay aligned with project updates, evolving guidelines, and new technical requirements. This collaboration includes occasional feedback sessions, error reviews, and pilot project evaluations to maintain content quality and consistency.
- Independent Workflow
The majority of the work involves independent tasks, such as writing, editing, and verifying AI-generated content. AI Editors typically dedicate about six focused hours each day to these responsibilities, working with technical specifications and project goals as their primary guidelines.
- Flexible Work Hours
While daily and weekly productivity targets must be met, the role offers significant flexibility in scheduling. Editors can choose their most productive working hours, allowing for a work-life balance while meeting project deadlines.
- Dynamic Tasks and Adaptability
Projects often involve rapidly changing requirements, which means editors must adapt to new guidelines and technical standards efficiently. This dynamic nature keeps the role engaging but requires a high level of flexibility and focus.
- Remote Work Opportunities
AI Editor positions are often remote, allowing professionals to work from anywhere. This arrangement adds to the role's appeal, particularly for those who value location independence.
What We Look for in AI Editors
When hiring for this position, our company prioritizes candidates who:
- Are detail-oriented and capable of critical thinking.
- Demonstrate patience and adaptability.
- Have strong written communication skills, ensuring polished and accurate content delivery.
Team Structure in Our AI Operations: Editors, Validators, and Assessors
In our company, the structure of AI operational teams ensures seamless handling of diverse tasks involved in refining and managing AI systems. We employ a multi-tiered team structure comprising Editors, Validators, and Assessors, with each playing distinct roles while collaborating across projects. Here’s a breakdown:
- The Editor Team
AI Editors form the core of our operational tasks. Their primary focus lies in refining AI-generated content and preparing high-quality datasets for AI training. They are the talent pool from which Validators are often promoted after proving their competence.
- The Validator Team
Validators ensure the accuracy, structure, and compliance of outputs. They are often aligned with specific editors or teams but can also be redistributed across projects as needed. This flexibility ensures efficient use of resources for time-sensitive or specialized tasks.
- The Role of AI Assessors
AI Assessors bridge gaps across multiple projects. Unlike Editors and Validators, they do not specialize in refinement or validation, but instead focus on data annotation tasks essential for training AI models.
5. Career Prospects for AI Trainer and Continuous Learning
Salary Ranges for AI Trainers and Editors
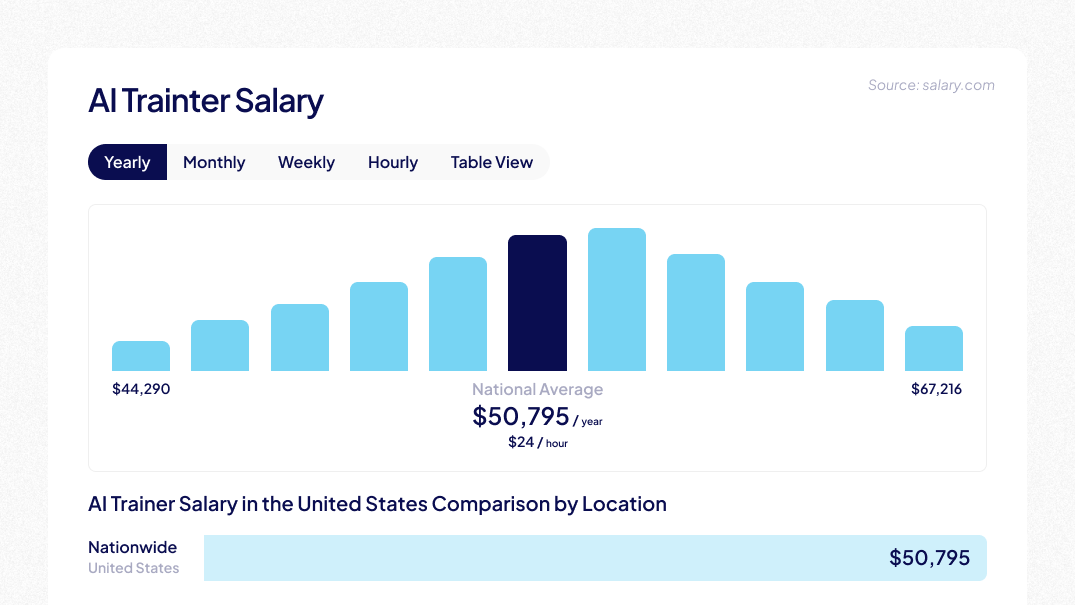
- AI Trainers: Salaries typically range from $40,000 to 90,000 per year, depending on experience, technical proficiency, and project complexity according to Coursera.

AI Editors and Validators: Professionals in AI editing and validation roles can expect to earn between $45,000 and 100,000 annually, with higher salaries for those specializing in complex AI systems and quality control.
Here are trusted platforms to explore AI Trainer and AI Editor positions:
- LinkedIn Jobs
- Indeed
- Glassdoor
- AngelList for startup-focused AI roles
- Remote.io for remote AI job opportunities
Continuous Learning for Growth
To excel in AI training and editing, continuous learning is essential. Professionals can enhance their skills through platforms like:
- Coursera – Offers AI and machine learning certifications.
- edX – Provides technical courses from top universities.
- Udacity – Specializes in AI and data science nanodegrees.
Conclusion
AI Trainers are pivotal in transforming the potential of AI into tangible, human-centered solutions. Their ability to blend technical rigor with ethical responsibility is shaping the future of AI. For aspiring professionals, this career offers not just job security but the opportunity to influence transformative technologies that impact millions of lives.
As industries continue to embrace AI, the demand for skilled Trainers will only grow. Whether you’re looking to start a career in AI or advance your current expertise, there’s never been a better time to invest in this dynamic field.