Lidar Annotation Services
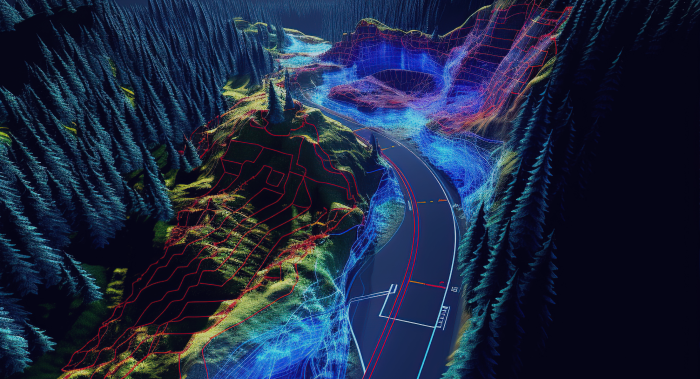
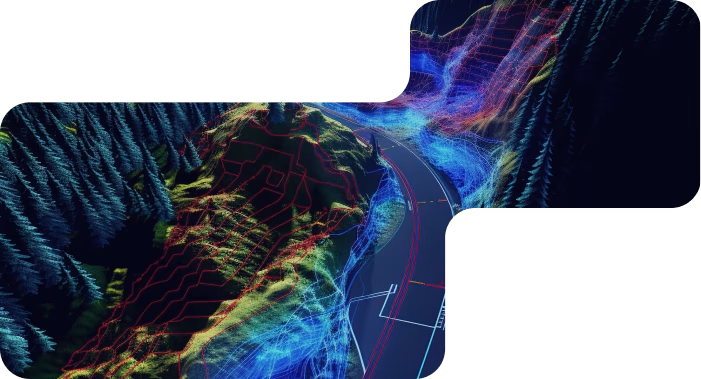
Unidata provides a comprehensive suite of services for precise LIDAR point cloud annotation, guaranteeing the creation of high-quality training datasets tailored for sophisticated machine learning applications. Our meticulous approach ensures that your datasets meet the specific requirements needed to enhance model performance and accuracy
Trusted by the world’s leading tech brands



24/7*
- 6+
- years experience with various projects
- 79%
- Extra growth for your company.
What is LIDAR Annotation?
LIDAR annotation is the process of labeling and tagging data derived from Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) technology to enhance the understanding and usability of three-dimensional spatial information. This involves marking various elements within LIDAR point clouds, such as terrain features, buildings, vegetation, and other significant structures, allowing for precise analysis and interpretation of the data.
LIDAR annotation is invaluable across numerous applications, including autonomous vehicle navigation, environmental monitoring, urban planning, and construction management.
How we deliver Lidar services
The best software for Lidar annotation tasks
Types (forms) of Lidar annotation services

3D Bounding Box Annotation
This form of annotation involves drawing 3D boxes around objects in LiDAR point clouds. It is used to define the spatial dimensions of objects like vehicles, pedestrians, buildings, or other objects of interest. This is especially important in autonomous driving, robotics, and other applications requiring object detection and classification.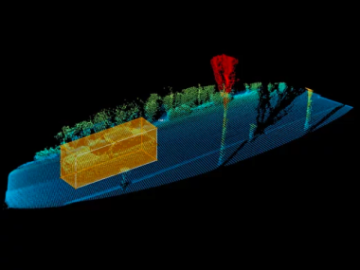
Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation is the process of classifying each individual point in a LiDAR point cloud into specific categories or classes. For example, points can be labeled as road surfaces, vehicles, trees, pedestrians, buildings, etc. This type of annotation is used for tasks like scene understanding, environmental mapping, and smart city planning.
Instance Segmentation
Instance segmentation is similar to semantic segmentation but involves identifying individual instances of objects within a scene. Instead of labeling all vehicles as "car," for example, each individual vehicle is labeled as a separate instance. This is useful for scenarios that require tracking and identifying multiple objects separately, such as autonomous vehicle navigation.
Polyline Annotation
Polyline annotation involves drawing lines to represent road lanes, boundaries, or paths within a LiDAR point cloud. This type of annotation is crucial for mapping road networks, lane marking detection in autonomous vehicles, and infrastructure planning for smart cities.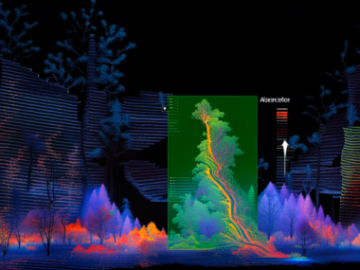
Point Annotation
Point annotation is used to mark specific key points of interest within a LiDAR point cloud. It can be used to pinpoint landmarks, track critical object locations, or identify specific areas within a larger dataset. This is often used in applications where exact locations of key features are required, such as in environmental monitoring and construction.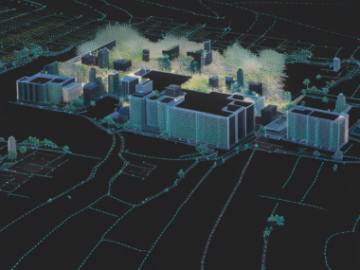
2D Projection from 3D Point Clouds
This type of annotation involves projecting 3D LiDAR point cloud data onto 2D images to enable 2D labeling. It combines the spatial accuracy of LiDAR data with the simplicity of 2D image annotation, typically used in cases where the user wants to combine visual and LiDAR information for enhanced perception.
Cuboid Annotation
Similar to 3D bounding boxes, cuboid annotation focuses on identifying and labeling objects with cuboids that account for the depth, width, and height of the object. It’s often used to label vehicles, pedestrians, and other objects in complex 3D spaces, providing rich data for 3D object detection models.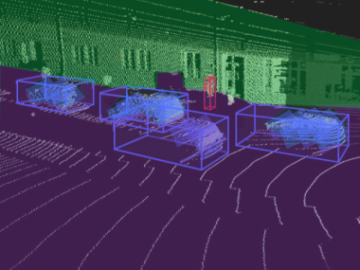
Environmental Object Annotation
Environmental object annotation involves labeling non-dynamic elements within a LiDAR point cloud, such as buildings, trees, fences, or roads. This form of annotation is used in applications like city planning, infrastructure development, and environmental monitoring, where a detailed understanding of static surroundings is crucial.3D Object Tracking
This type of annotation involves labeling objects across multiple frames to track their movement through space. It is especially important in scenarios such as autonomous driving, where continuous tracking of vehicles, pedestrians, and other objects is essential for decision-making and navigation.
Terrain and Elevation Annotation
This form of annotation focuses on labeling elevation and terrain-related data, which can include hills, valleys, cliffs, and other geographical features. It is often used in topographical mapping, surveying, and environmental monitoring.Lidar Annotation Use Cases
-
 01
01Construction & Architecture
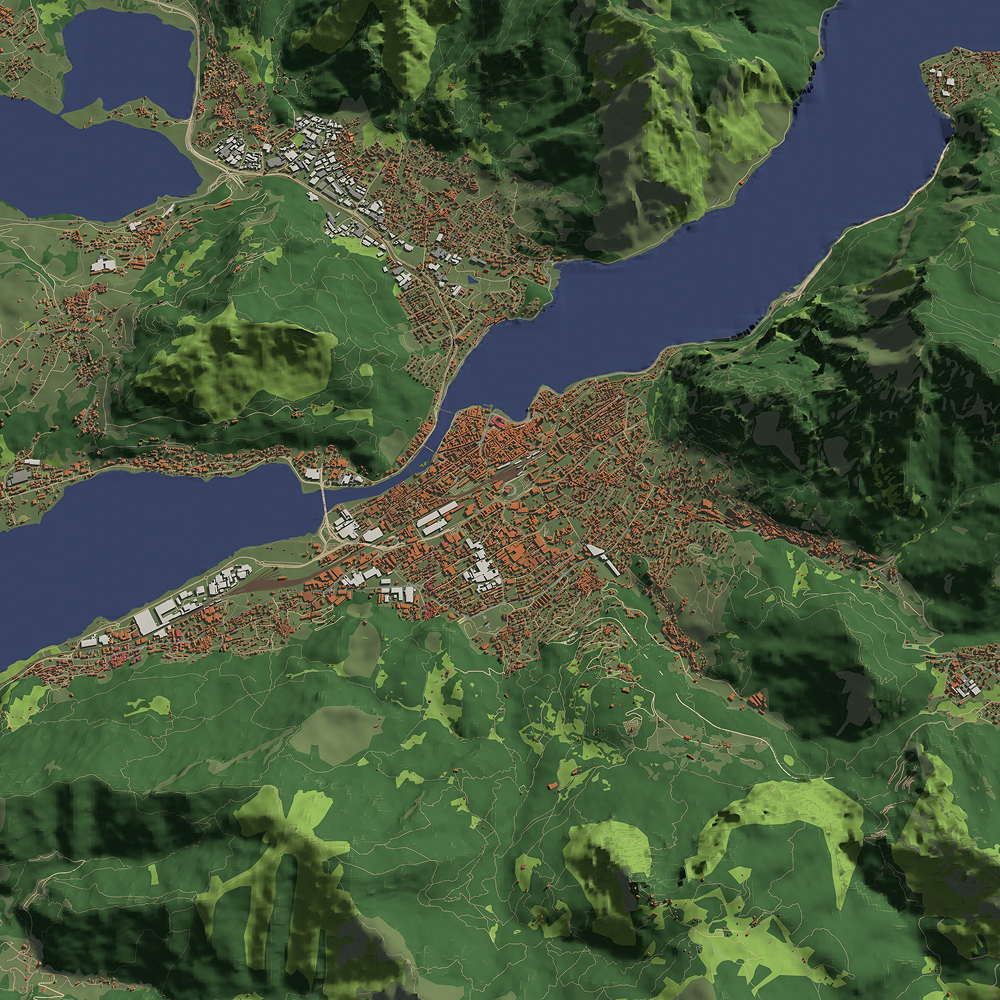
In construction and architecture, LiDAR annotation is used to create accurate 3D models of buildings, construction sites, and infrastructures. By labeling point clouds with information about building materials, dimensions, and structural components, AI can assist in the planning, design, and monitoring of construction projects. LiDAR data also helps with site inspections and ensures that designs meet building codes and specifications. -
 02
02Environmental Monitoring
In environmental monitoring, this service is used to analyze changes in landscapes, forests, or coastal regions. By labeling point clouds of terrain or vegetation, AI can track environmental changes, such as deforestation, erosion, or flood risks. Annotated LiDAR data helps in assessing the impact of climate change, supporting conservation efforts, and improving environmental management strategies. -
 03
03Healthcare
LiDAR labeling helps to create 3D models for medical imaging, such as MRI or CT scans. By annotating data from 3D scans of organs, bones, or tissues, AI systems can assist doctors in diagnosing conditions like tumors, fractures, and abnormal growths. LiDAR-based models allow for more accurate visualization of complex structures, enabling precise surgical planning and better patient care. -
 04
04Agriculture
In agriculture, Light Detection and Ranging annotation help monitor land and crop conditions by creating detailed 3D maps of fields. By annotating areas affected by pests, diseases, or irregularities in soil, AI can analyze crop health and optimize farming practices. LiDAR data helps farmers identify areas that need attention, enabling more efficient use of resources such as water, fertilizer, and pesticides. -
 05
05Real Estate
LiDAR annotation in real estate is used to create 3D models of properties and land. By labeling LiDAR data with attributes such as the size of rooms, location of amenities, and the layout of properties, AI can enhance property listings and improve virtual tours. This data also helps developers and buyers visualize spaces more accurately, aiding in better decision-making when purchasing or designing properties. -
 06
06Security & Surveillance
It is used to improve monitoring systems by labeling 3D data from surveillance areas. By annotating LiDAR point clouds with information about objects like vehicles, people, or restricted zones, AI can better track movements and detect potential security threats. This helps security teams monitor large areas in real time, improving situational awareness and response times. -
 07
07Manufacturing
This service helps in manufacturing for quality control and warehouse management. By annotating 3D scans of products, machines, or production lines, AI systems can detect defects, misalignments, or wear and tear. LiDAR data also helps in optimizing layout planning for factories or warehouses, ensuring better organization and more efficient workflows. -
 08
08Automotive (Autonomous Vehicles)
LiDAR annotation is essential for autonomous vehicles to understand their surroundings. By annotating LiDAR point clouds with labels for objects such as pedestrians, vehicles, traffic signs, and road markings, AI systems can accurately perceive the environment in 3D. This data helps autonomous vehicles navigate safely, detect obstacles, and make real-time driving decisions, ensuring safer travel.
Other Services
Ready to get started?
Tell us what you need — we’ll reply within 24h with a free estimate

- Andrew
- Head of Client Success
— I'll guide you through every step, from your first
message to full project delivery
Thank you for your
message
We use cookies to enhance your experience, personalize content, ads, and analyze traffic. By clicking 'Accept All', you agree to our Cookie Policy.




















