Geospatial Annotation services

Unidata provides Geospatial Annotation Services, delivering accurate labeling and tagging of geospatial data to improve mapping, navigation, and spatial analysis across multiple industries and applications. Our expert team ensures high-quality annotations that enhance the effectiveness of your geospatial projects
Trusted by the world’s leading tech brands




Advantages
SLA over projects
24/7*
24/7*
- 6+
- years experience with various projects
- 79%
- Extra growth for your company.
Geospatial Annotation
What is Geospatial Annotation?
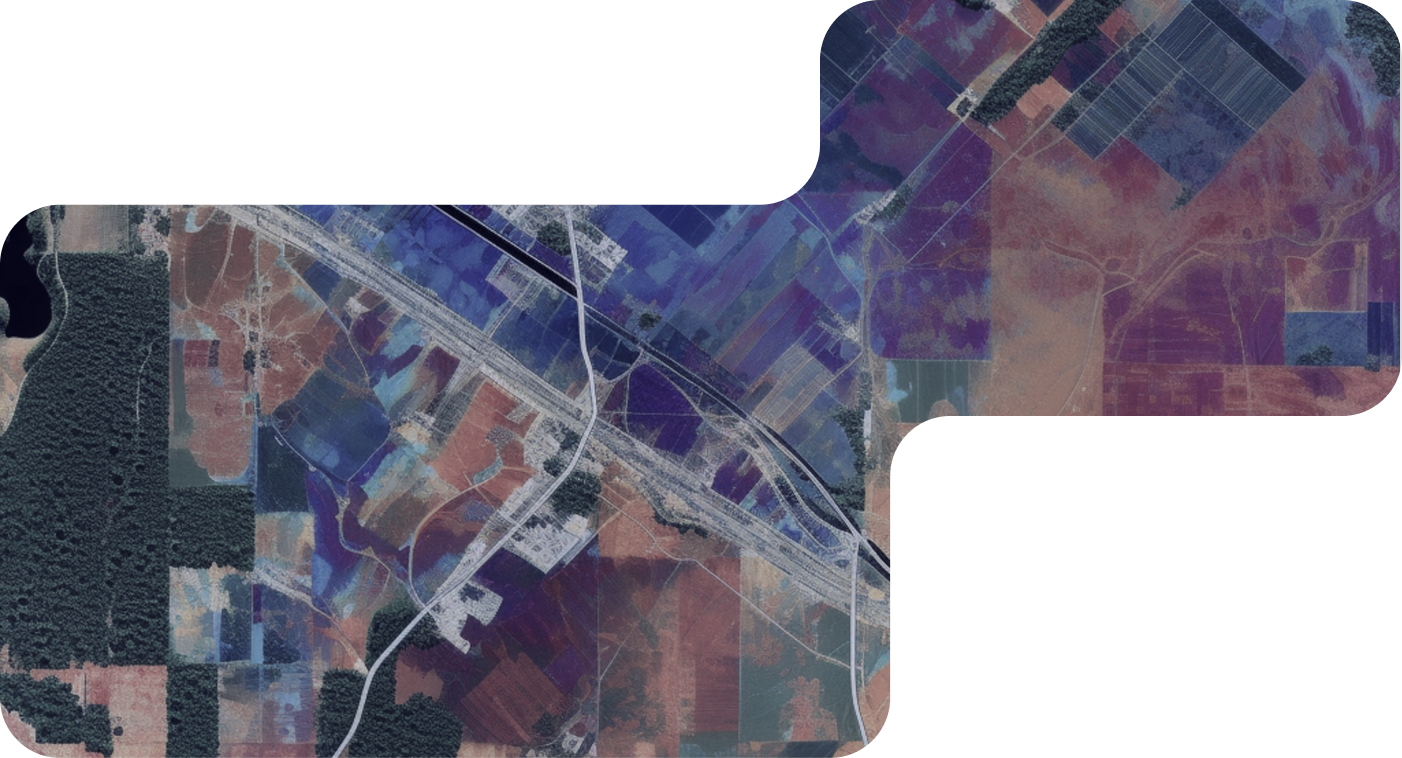
Geospatial annotation in data training services involves accurately labeling and tagging geographic information within datasets, such as maps, satellite images, or aerial photographs. This process assigns descriptive metadata to geographic features, such as roads, buildings, land cover types, or points of interest, facilitating spatial analysis, mapping, and navigation applications for various industries and use cases.Types of Geospatial Annotation Services

Land Cover Classification
Land cover classification annotation involves categorizing land surface types, such as forests, water bodies, urban areas, and agricultural land, within satellite or aerial imagery. Annotations enable mapping and monitoring changes in land cover over time, supporting environmental management and resource planning.
Object Detection and Segmentation
Object detection and segmentation annotation entails identifying and delineating specific objects or features within geospatial datasets, such as buildings, roads, vehicles, or vegetation. Annotations provide precise boundaries or polygons around objects of interest, facilitating automated feature extraction and analysis.
Point of Interest (POI) Annotation
Point of Interest (POI) annotation involves identifying and labeling points of interest within geographic datasets, such as landmarks, businesses, tourist attractions, or public amenities. Annotations provide descriptive metadata for each POI, supporting location-based services, navigation, and tourism applications.
Route and Path Annotation
Route and path annotation entails tracing and annotating routes, trails, or pathways within maps or GPS trajectories. Annotations define the spatial geometry and attributes of routes, facilitating navigation, route planning, and outdoor recreation activities.
Geospatial Attribute Tagging
Geospatial attribute tagging annotation involves assigning descriptive attributes or characteristics to geographic features, such as elevation, slope, land use, or administrative boundaries. Annotations provide additional contextual information for spatial analysis, modeling, and decision-making processes.
Landmark Recognition and Localization
Landmark recognition and localization annotation entails identifying and annotating prominent landmarks or features within geospatial datasets, such as mountains, rivers, monuments, or buildings. Annotations enable accurate landmark detection and navigation guidance in mapping and location-based applications.
Change Detection and Monitoring
Change detection and monitoring annotation involve comparing multiple geospatial datasets over time to identify and annotate areas of change, such as land cover change, urban expansion, or infrastructure development. Annotations support monitoring environmental trends, assessing habitat loss, and detecting natural disasters.
Boundary and Parcel Annotation
Boundary and parcel annotation entails delineating and annotating property boundaries, land parcels, or administrative boundaries within cadastral maps or property surveys. Annotations provide accurate spatial information for land management, cadastral mapping, and real estate applications.
Remote Sensing Image Annotation
Remote sensing image annotation involves labeling features and phenomena observed in satellite or aerial imagery, such as clouds, water bodies, vegetation indices, or geological formations. Annotations support environmental monitoring, disaster response, and natural resource management initiatives.
Street View Annotation
Street view annotation entails annotating street-level imagery with features like road signs, traffic lights, pedestrian crossings, and building facades. Annotations enhance the accuracy of navigation systems, urban planning, and location-based services in urban environments.How we Deliver Geospatial Annotation Projects
At Unidata, we are committed to delivering Geospatial Annotation Projects with precision, efficiency, and client satisfaction as our top priorities. Our process encompasses several key stages, each meticulously designed to ensure accuracy, quality, and timely delivery.-
01.
Project Scoping and Consultation
We begin by engaging in detailed consultations with you to understand your project requirements, specific annotation tasks, and desired outcomes. This phase allows us to tailor our approach to meet your unique needs and objectives. -
02.
Data Collection and Preprocessing
With the project scope defined, we collect the necessary geospatial data, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, or GIS datasets, and preprocess it as needed. This may involve image rectification, enhancement, and spatial referencing to optimize data quality and annotation efficiency. -
03.
Annotation Methodology Selection
Based on the insights gathered during the consultation phase, we select the most appropriate annotation methodologies and tools for your geospatial data annotation tasks. Our experienced team evaluates factors such as data complexity, annotation requirements, and industry standards to determine the optimal approach. -
04.
Annotation Execution
Our skilled annotators then meticulously execute the geospatial annotation tasks according to the predefined guidelines and criteria. Annotations may include delineating land cover types, tracing road networks, identifying points of interest, or labeling objects within satellite imagery.
Geospatial Annotation Use Cases
-
 01
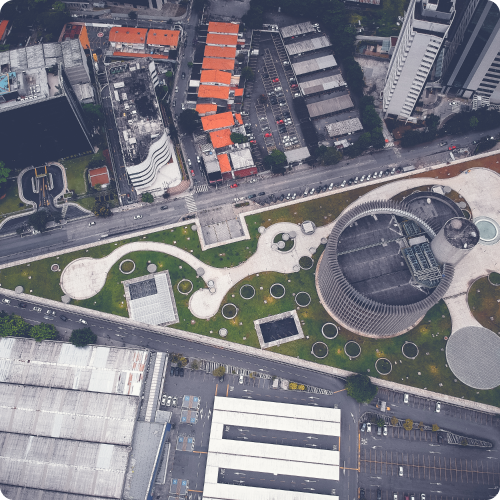
01Urban Planning and Development
Urban planning agencies use geospatial annotation data to map land use, transportation networks, and infrastructure facilities. Annotations aid in identifying suitable locations for development projects, assessing environmental impacts, and optimizing urban growth strategies. -
 02
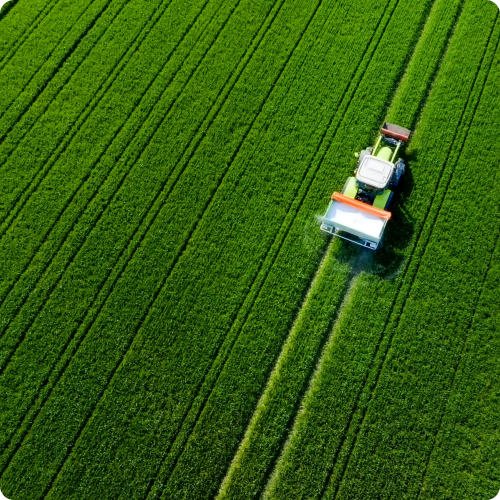
02Precision Agriculture
Agriculture companies leverage geospatial annotation data to monitor crop health, soil moisture levels, and pest infestations. Annotations enable precision farming techniques, such as variable rate application of fertilizers and pesticides, leading to improved crop yields and resource efficiency. -
 03
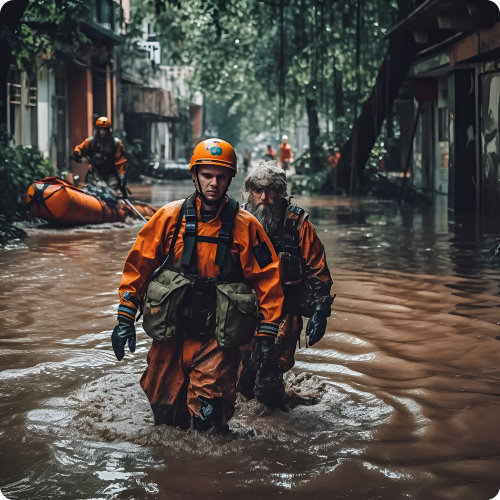
03Disaster Response and Emergency Management
Emergency response organizations utilize geospatial annotation data to map disaster-affected areas, assess damage severity, and plan rescue operations. Annotations aid in identifying evacuation routes, locating emergency shelters, and coordinating relief efforts during natural disasters or humanitarian crises. -
 04
04Environmental Conservation and Management
Environmental agencies rely on geospatial annotation data to monitor wildlife habitats, biodiversity hotspots, and protected areas. Annotations facilitate habitat mapping, species tracking, and ecosystem monitoring, supporting conservation efforts and sustainable resource management. -
 05
05Infrastructure Maintenance and Asset Management
Utility companies use geospatial annotation data to inventory infrastructure assets, such as power lines, pipelines, and telecommunications networks. Annotations aid in asset tracking, condition assessment, and maintenance planning, ensuring reliable service delivery and infrastructure resilience. -
 06
06Real Estate and Property Management
Real estate firms leverage geospatial annotation data to assess property values, analyze market trends, and identify investment opportunities. Annotations enable visualizing property boundaries, zoning regulations, and neighborhood amenities, supporting property valuation and site selection processes. -
 07
07Natural Resource Exploration and Mining
Mining companies utilize geospatial annotation data to identify mineral deposits, plan extraction operations, and assess environmental impacts. Annotations aid in geological mapping, resource estimation, and mine site rehabilitation, ensuring responsible resource extraction and land reclamation. -
 08
08Transportation and Logistics
Transportation companies rely on geospatial annotation data to optimize route planning, track vehicle movements, and monitor supply chain operations. Annotations enable real-time vehicle tracking, congestion management, and delivery route optimization, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Other Services
Ready to get started?
Tell us what you need — we’ll reply within 24h with a free estimate

- Andrew
- Head of Client Success
— I'll guide you through every step, from your first
message to full project delivery
Thank you for your
message
We use cookies to enhance your experience, personalize content, ads, and analyze traffic. By clicking 'Accept All', you agree to our Cookie Policy.



