NLP Annotation services

Unidata proudly offers advanced NLP Annotation Services, specializing in the precise labeling and tagging of textual data to significantly enhance the accuracy and performance of natural language processing (NLP) models.
Trusted by the world’s leading tech brands




Advantages
SLA over projects
24/7*
24/7*
- 6+
- years experience with various projects
- 79%
- Extra growth for your company.
NLP Annotation
What is NLP Annotation?
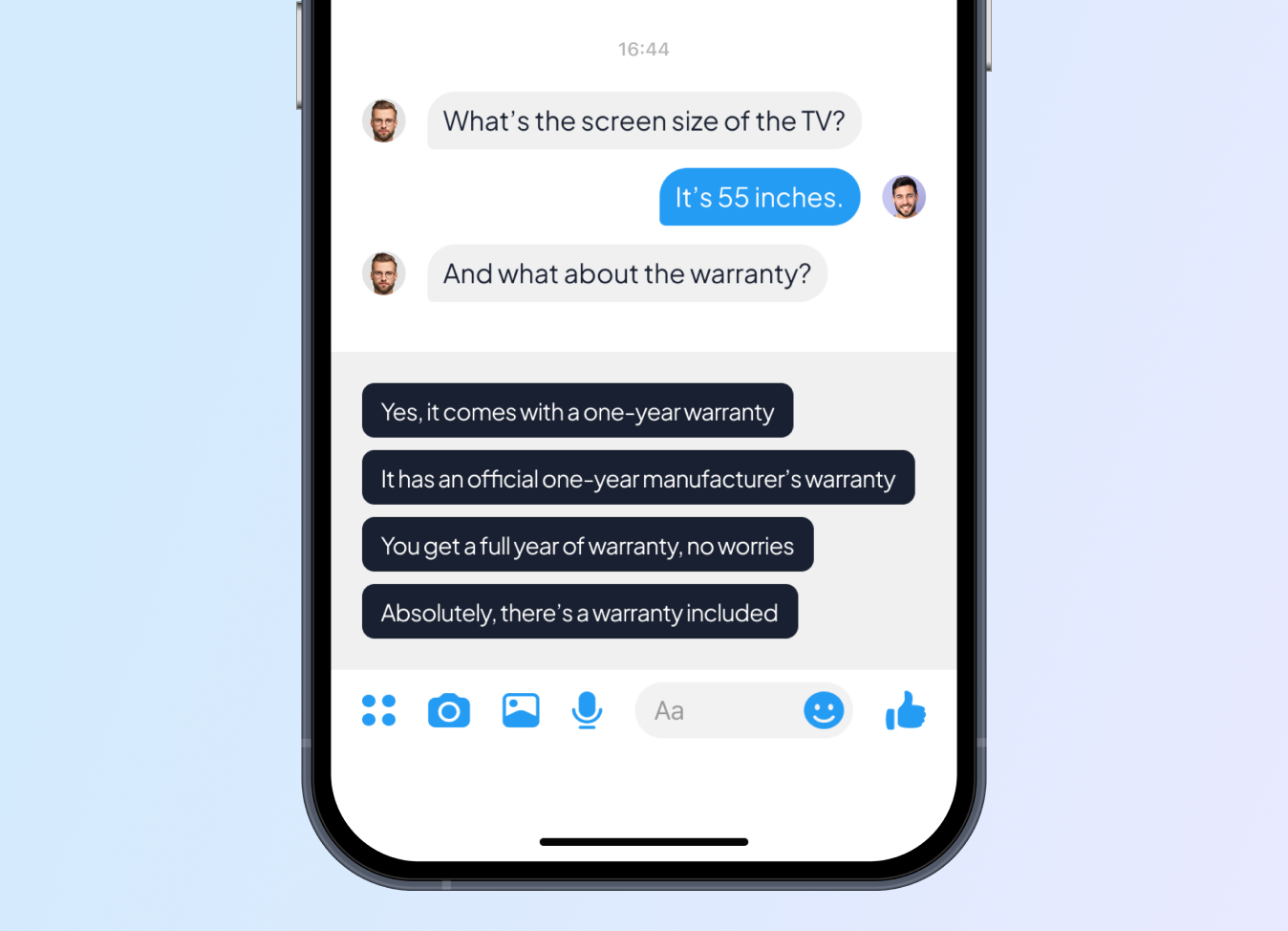
NLP (Natural Language Processing) annotation is the process of labeling and tagging various elements within textual data to improve the performance and accuracy of NLP models. This involves identifying and classifying components such as entities, sentiments, intents, parts of speech, and relationships within the text. By transforming unstructured data into structured formats, NLP annotation enables machine learning algorithms to understand the intricacies of human language, facilitating tasks such as sentiment analysis, machine translation, chatbots, and information extraction.Types of NLP Annotation Services

Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging
POS tagging involves annotating each word in a text with its corresponding grammatical category, such as noun, verb, adjective, or adverb. These annotations provide linguistic insights into the syntactic structure of the text, facilitating tasks like parsing and information extraction.
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
NER annotation identifies and classifies named entities within text, such as names of people, organizations, locations, dates, and numerical expressions. Annotations enable extraction of structured information from unstructured text data, supporting tasks like entity linking and knowledge graph construction.
Syntactic Parsing
Syntactic parsing annotates the grammatical structure of sentences, including dependencies between words and phrases. Annotations provide a hierarchical representation of the text's syntactic relationships, aiding in tasks like semantic analysis, question answering, and machine translation.
Title Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis annotation assigns sentiment labels (e.g., positive, negative, neutral) to text, indicating the emotional tone expressed by the author. Annotations enable automated understanding of opinions, attitudes, and emotions conveyed in text, supporting applications like social media monitoring and customer feedback analysis.
Coreference Resolution
Coreference resolution annotation identifies and links referring expressions (e.g., pronouns, definite noun phrases) to their corresponding antecedents within text. Annotations help resolve ambiguous references and establish coherence in discourse, improving the performance of tasks like text summarization and document understanding.
Semantic Role Labeling (SRL)
SRL annotation identifies the semantic roles played by different constituents of a sentence, such as agents, patients, and instruments. Annotations capture the predicate-argument structure of sentences, facilitating tasks like information extraction, question answering, and semantic parsing.
Temporal Expression Recognition
Temporal expression recognition annotation identifies and annotates temporal expressions (e.g., dates, times, durations) within text. Annotations enable extraction of temporal information for tasks such as event extraction, temporal reasoning, and timeline generation.
Event Extraction
Event extraction annotation identifies and extracts events mentioned in text, including event triggers, participants, and temporal attributes. Annotations capture the semantics of events, supporting tasks like event clustering, trend analysis, and event-driven information retrieval.NLP Annotation Use Cases
-
 01
01Healthcare
In healthcare, NLP annotation helps train AI to understand medical texts such as clinical notes, research papers, and Electronic Health Records (EHR). Labeling key terms such as symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans allows AI to assist doctors in diagnosing conditions more accurately. Annotating patient histories enables AI to predict potential health outcomes and suggest better treatment strategies, improving overall patient care. -
 02
02Automotive (Autonomous Vehicles)
In the automotive industry, this type of annotation plays an important role in teaching self-driving cars to understand road signs, traffic signals, and spoken commands. Labeling text data from navigation systems allows AI to process instructions and respond to real-time driving conditions. Annotating pedestrian behavior and traffic-related texts enables the AI to anticipate hazards and navigate safely. -
 03
03Retail & E-commerce
Annotation is used to categorize product descriptions, customer reviews, and sales data. Labeling product features, sentiment in reviews, and customer preferences help AI enhance search functionality and improve product recommendations. Annotating feedback with specific keywords enables businesses to optimize marketing strategies and inventory management, catering to customer needs more effectively. -
 04
04Agriculture
In agriculture, it is used to analyze agricultural reports, research articles, and sensor data. Labeling terms related to crop health, pests, weather conditions, and soil quality allows AI to assist farmers in making data-driven decisions. Annotating data related to farming practices helps AI optimize irrigation, pest control, and crop rotation strategies, contributing to better yields and resource management. -
 05
05Finance
This service helps process and analyze financial reports, transaction logs, and customer data. Labeling key information like transaction types, account details, and spending patterns helps AI detect fraud, assess financial risks, and improve credit scoring. Annotating investment reports and contracts allows AI to extract relevant data, enhancing the speed and accuracy of financial decision-making. -
 06
06Security & Surveillance
NLP annotation plays a crucial role in security and surveillance systems by labeling texts from video transcripts, incident reports, and security alerts. Labeling suspicious activities, locations, and individuals allows AI to detect potential threats in real time. Annotating crime reports or witness statements helps AI systems generate actionable insights and improve response times for law enforcement. -
 07
07Manufacturing
NLP labeling is used to label maintenance logs, product descriptions, and quality control documents. Labeling critical information such as defect types, machine performance, and assembly processes helps AI predict equipment failures and improve quality assurance. Annotating operational manuals assists AI in automating tasks, reducing human error, and optimizing workflows in production lines. -
 08
08Entertainment & Media
In the entertainment industry, NLP is applied to analyze scripts, social media posts, and video content. Labeling specific themes, emotions, or actions in text allows AI to help with content recommendations, content moderation, and audience engagement. Annotating reviews and feedback with sentiment data helps businesses refine their marketing strategies and adapt to audience preferences.
Other Services
Ready to get started?
Tell us what you need — we’ll reply within 24h with a free estimate

- Andrew
- Head of Client Success
— I'll guide you through every step, from your first
message to full project delivery
Thank you for your
message
We use cookies to enhance your experience, personalize content, ads, and analyze traffic. By clicking 'Accept All', you agree to our Cookie Policy.
Ready to get started?
Tell us what you need — we’ll reply within 24h with a free estimate