In the ever-evolving landscape of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), quality data is king. The performance of models, whether for computer vision, natural language processing, or other domains, heavily relies on accurate annotations. Annotation tools serve as the bridge between raw data and actionable insights, enabling ML practitioners to label datasets efficiently and effectively.
With numerous annotation tools available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. This guide delves into the 15 best annotation tools of 2025, offering an in-depth exploration of their features, use cases, and suitability for various tasks. Whether you’re an experienced Data Scientist, a budding ML enthusiast, or a newcomer, this list will help you navigate the options and make an informed decision.
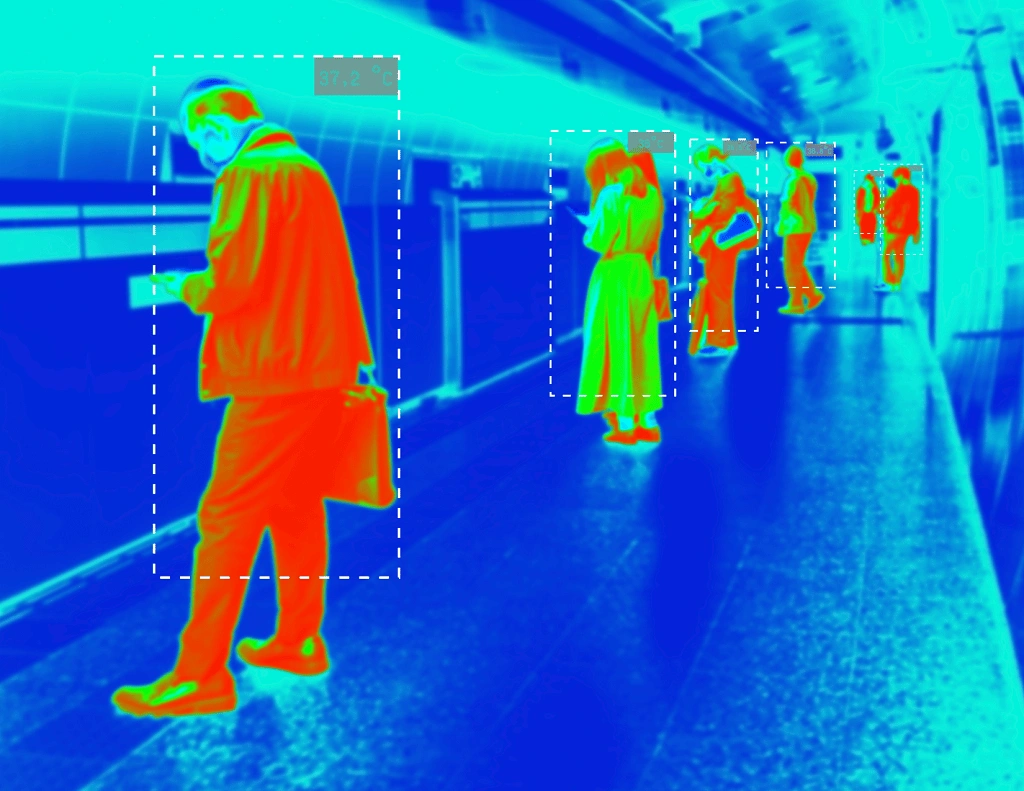

What Are Annotation Tools?
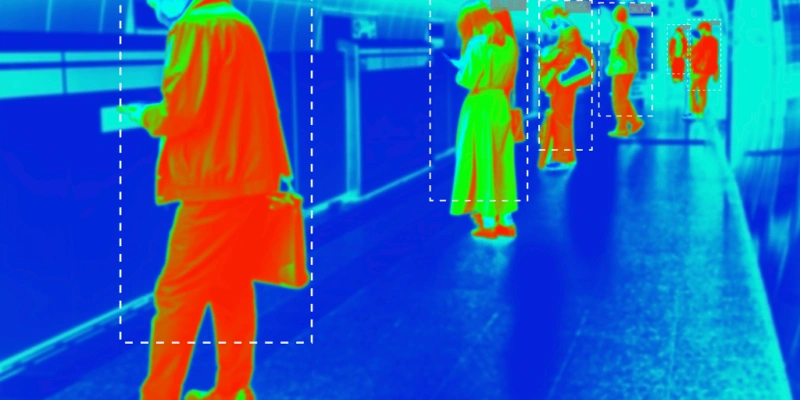
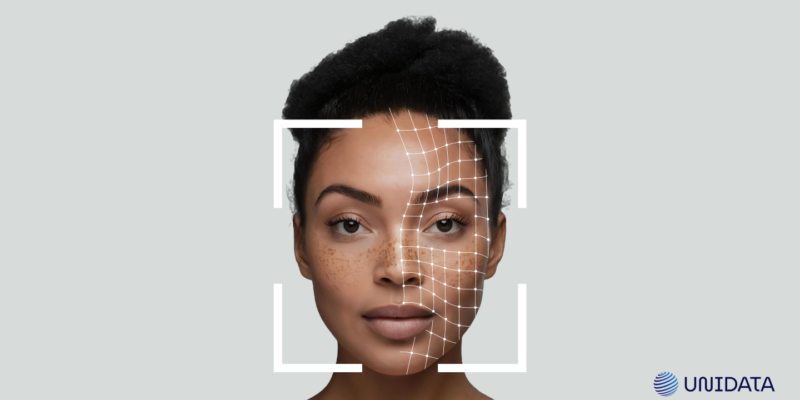
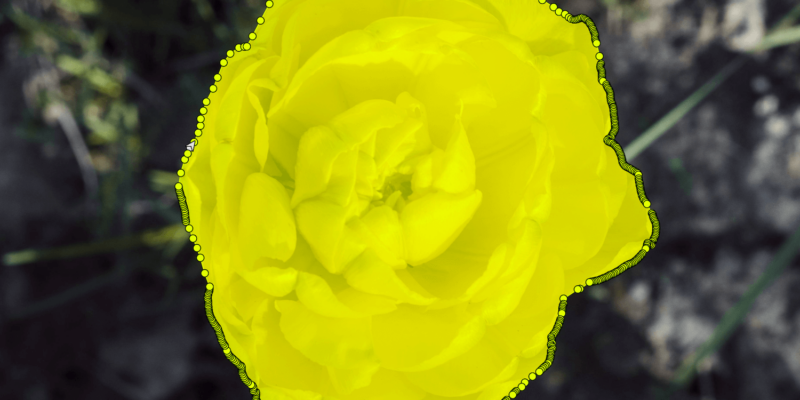
Annotation tools are software platforms designed to label diverse types of data, including images, videos, text, or audio, for training ML models. They offer functionalities such as bounding boxes, polygons, semantic segmentation, and keypoint annotations, tailored to specific data needs.
These tools play a pivotal role in:
- Streamlining annotation workflows.
- Enhancing labeling accuracy.
- Accelerating project timelines while reducing costs.
How to Choose the Right Annotation Tool
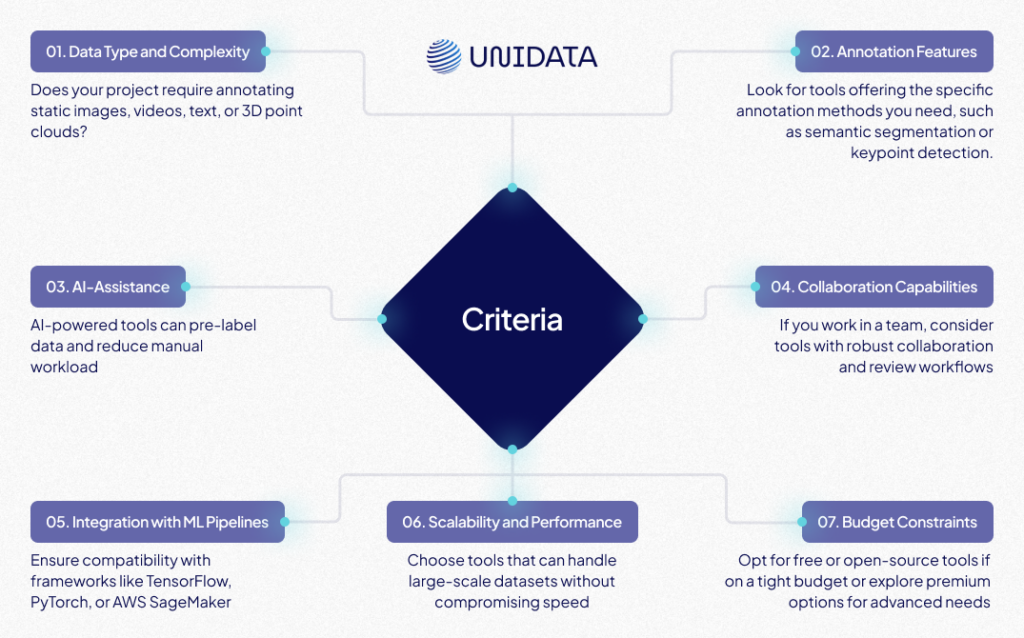
Selecting the right annotation tool involves evaluating multiple criteria to align with your project’s requirements:
1. CVAT
Description: The Computer Vision Annotation Tool (CVAT) is an open-source, web-based annotation tool tailored for computer vision projects. Developed by Intel, it offers flexibility and efficiency for various annotation needs, from simple bounding boxes to complex segmentation tasks.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images and video annotations, including 2D bounding boxes, polygons, and semantic segmentation.
- Annotation Features: Advanced tools like interpolation for video annotations and frame-wise adjustments.
- AI-Assistance: Includes semi-automatic annotation features to expedite workflows.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Seamlessly integrates with frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Scalability and Performance: Handles large-scale projects with ease, suitable for enterprise and individual use.
Collaboration: Facilitates team-based annotations with options for role-based access control and task management.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Free, open-source, and highly customizable.
- Cons: Requires some technical expertise to set up and manage.
Export Formats: COCO, Pascal VOC, YOLO, and custom formats.
Pricing: Free and open-source.
Use Cases: Ideal for academic research, startups, and enterprises working on computer vision projects like object detection and segmentation.
2. Label Studio

Description:
Label Studio is an open-source data labeling tool designed for machine learning and data science projects. It supports a wide range of annotation types and integrates seamlessly with various ML pipelines.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images, audio, text, and video annotations, capable of handling tasks like image segmentation, object detection, and text classification.
- Annotation Features: Customizable interface with an extensive set of annotation tools, such as bounding boxes, polygons, and text tagging.
- AI-Assistance: Active learning capabilities to enhance and speed up the annotation process by incorporating machine learning models.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Smooth integration with frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
- Scalability and Performance: Handles large datasets efficiently, supporting team collaboration for large projects.
- Collaboration: Features role-based access control, allowing team members to work together with varying permissions.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Highly flexible and customizable, supports multiple data types, integrates easily with ML workflows.
- Cons: Initial setup and configuration can be time-consuming and requires some technical expertise.
Export Formats:
COCO, CSV, JSON, and other custom formats.
Pricing:
Free (open-source), with paid enterprise options available.
Use Cases:
Ideal for projects requiring a variety of data types, such as image classification, object detection, speech recognition, and natural language processing tasks.
3. V7

Description: V7 is a commercial annotation platform known for its automation and AI-assisted labeling capabilities. Its focus on enterprise-grade features makes it a preferred choice for large-scale projects.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Handles images, videos, and 3D point clouds.
- Annotation Features: Offers advanced annotation tools like keypoints, polylines, and 3D cuboids.
- AI-Assistance: Features automated labeling, model-assisted annotations, and active learning.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Integrates seamlessly with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and REST APIs.
- Scalability and Performance: Optimized for handling large datasets with high efficiency.
Collaboration: Provides team management tools, including task assignments and review processes.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Exceptional automation capabilities and robust performance.
- Cons: High cost for enterprise features.
Export Formats: COCO, YOLO, Pascal VOC, and custom formats.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on usage.
Use Cases: Ideal for enterprises focusing on autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and large-scale data labeling projects.
4. SuperAnnotate

Description: SuperAnnotate is a comprehensive platform designed for efficient team collaboration and AI-assisted annotation. Its focus on project management makes it an excellent choice for enterprises.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images, videos, and document annotation.
- Annotation Features: Bounding boxes, polygons, and pixel-perfect segmentation.
- AI-Assistance: Features auto-labeling and active learning for rapid dataset creation.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Direct integrations with popular ML platforms and APIs.
- Scalability and Performance: Handles high-volume datasets efficiently.
Collaboration: Enables team collaboration with features like quality control and task management.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Excellent collaboration tools and intuitive interface.
- Cons: Pricing may be prohibitive for smaller teams.
Export Formats: JSON, COCO, and custom formats.
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request.
Use Cases: Best suited for medical imaging, document analysis, and enterprise-grade computer vision projects.
5. Labelbox

Description: Labelbox is a widely-used data annotation platform tailored for scalability and collaboration. With its intuitive design and robust AI-assisted features, it simplifies data labeling for large-scale ML projects. Pro tip: Labelbox's workflow customization allows users to optimize task assignments for increased efficiency.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports image, video, text, and geospatial data.
- Annotation Features: Offers bounding boxes, polygons, semantic segmentation, and text annotations.
- AI-Assistance: Provides automated pre-labeling, quality assurance workflows, and model-assisted labeling.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Integrates seamlessly with platforms like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and AWS SageMaker.
- Scalability and Performance: Optimized for large datasets with high processing efficiency.
Collaboration: Team-friendly features include task assignments, real-time collaboration, and built-in review workflows.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Exceptional user interface, comprehensive integrations, and robust support.
- Cons: Subscription pricing may be prohibitive for smaller teams.
Export Formats: JSON, COCO, Pascal VOC, and custom formats.
Pricing: Starts at $25,000 annually; custom enterprise plans available.
Use Cases: Best for enterprises handling diverse data types, such as autonomous vehicle companies and healthcare organizations.
6. Roboflow

Description:
Roboflow is an AI-powered annotation tool focused on simplifying the computer vision annotation process. It utilizes machine learning to enhance the efficiency of labeling tasks and integrates seamlessly with ML pipelines.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Specializes in images and videos, suitable for object detection, segmentation, and classification tasks.
- Annotation Features: Features auto-annotation tools that use AI to speed up the process and reduce manual input.
- AI-Assistance: AI-powered tools that help with auto-labeling and improve accuracy through machine learning models.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Works well with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and other popular frameworks for seamless integration.
- Scalability and Performance: Optimized for handling both small and large datasets with cloud-based infrastructure.
- Collaboration: Offers multi-user functionality with customizable roles for team management.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Fast, AI-driven annotation capabilities; easy-to-use interface.
- Cons: Limited support for non-image formats and occasional issues with large datasets.
Export Formats:
COCO, YOLO, TFRecord, and more.
Pricing:
Free tier with premium plans for advanced features.
Use Cases:
Ideal for computer vision tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, and image classification.
7. LabelImg

Description:
LabelImg is a graphical image annotation tool designed for labeling images with bounding boxes for object detection tasks. It’s open-source and widely used in computer vision projects.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Primarily for image annotation with a focus on bounding boxes for object detection.
- Annotation Features: Simple and intuitive interface for annotating images with bounding boxes, capable of creating XML files in Pascal VOC format.
- AI-Assistance: No AI assistance, purely manual annotation.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Exports annotations in formats compatible with most ML frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Scalability and Performance: Ideal for small to medium-sized datasets, but may require additional tools for large-scale projects.
- Collaboration: Does not have built-in collaboration features but supports sharing project files.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Free and open-source, easy to use for beginners.
- Cons: Limited to bounding box annotations, lacks advanced features like segmentation.
Export Formats:
Pascal VOC, YOLO, and others.
Pricing:
Starting price: Free (open-source).
Use Cases:
Best suited for small-scale object detection tasks and image labeling projects.
8. Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth

Description:
Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth is a fully managed data labeling service that uses machine learning to assist in the creation of high-quality datasets. It allows for human-in-the-loop labeling to accelerate ML model development.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images, video, text, and audio annotations for a variety of ML tasks like classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation.
- Annotation Features: Includes workflows for active learning, enabling machine learning models to label data with human review.
- AI-Assistance: Offers automatic labeling powered by ML models, which helps reduce the time needed for manual annotation.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Fully integrated with Amazon SageMaker and other AWS services for streamlined workflows.
- Scalability and Performance: Highly scalable, designed to handle large datasets efficiently.
- Collaboration: Supports team collaboration with user management and role-based access control.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Highly scalable, integrates with AWS, includes AI-powered annotation tools.
- Cons: Can become expensive, especially for large datasets.
Export Formats:
COCO, TFRecord, CSV, and more.
Pricing:
Starting price: Pay-as-you-go, with additional charges for human annotators and storage.
Use Cases:
Ideal for large-scale datasets requiring diverse annotation types, especially for enterprises using AWS infrastructure.
9. BasicAI

Description:
BasicAI is a data annotation platform that helps teams build machine learning models with human-in-the-loop data labeling and model training. It’s a flexible tool suitable for various types of annotations.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports image, video, and text annotation tasks, including classification, object detection, and named entity recognition.
- Annotation Features: Includes tools for both manual and automated annotations, with integration for custom tasks.
- AI-Assistance: Provides automated labeling with machine learning models to speed up the annotation process.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Seamless integration with popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Scalability and Performance: Suitable for both small and large-scale projects with cloud infrastructure support.
- Collaboration: Allows team collaboration with task management and role-based permissions.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Flexible, supports multiple data types, AI-powered annotation tools.
- Cons: Can require a learning curve for beginners.
Export Formats:
COCO, YOLO, Pascal VOC, and others.
Pricing:
Starting price: Custom pricing based on project needs.
Use Cases:
Good for companies and teams looking to manage multiple annotation types across various data formats.
10. Supervisely

Description:
Supervisely is an AI-based platform for data annotation and dataset management, primarily focused on computer vision tasks. It offers extensive features for both manual and semi-automated annotations.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images and videos, specializing in object detection, segmentation, and pose estimation tasks.
- Annotation Features: Offers tools for segmentation, bounding boxes, polylines, and more. It also supports 3D data annotations.
- AI-Assistance: Provides AI-assisted annotation tools to speed up the labeling process and improve accuracy.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Integrates well with ML frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras.
- Scalability and Performance: Highly scalable, designed for handling large datasets and projects with multiple users.
- Collaboration: Includes team collaboration features with role-based permissions and task management.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Robust and feature-rich, supports 3D annotations, AI-powered labeling.
- Cons: Interface may seem overwhelming for beginners.
Export Formats:
COCO, YOLO, Pascal VOC, and more.
Pricing:
Starting price: Free tier with paid plans for advanced features (custom pricing for enterprise).
Use Cases:
Ideal for large-scale computer vision projects involving segmentation, object detection, and 3D annotations.
11. Scale AI

Description: Scale AI specializes in delivering high-quality annotated data for training AI models, focusing on enterprise-level data management. Its focus on automation and AI-assisted features makes it a preferred choice for complex projects.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports image, video, text, and LiDAR point cloud annotations.
- Annotation Features: Provides tools for 3D cuboids, semantic segmentation, and text classification.
- AI-Assistance: Advanced features like automatic annotation and quality control powered by machine learning.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Compatible with major ML frameworks and APIs.
- Scalability and Performance: Designed for large-scale projects with demanding processing needs.
Collaboration: Built-in collaboration tools enable seamless workflows across teams and external contractors.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Highly reliable for large datasets, excellent quality assurance mechanisms.
- Cons: Expensive for small teams or academic use.
Export Formats: JSON, CSV, and proprietary formats.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on project requirements.
Use Cases: Ideal for industries like autonomous driving, financial services, and defense.
12. Dataloop

Description: Dataloop is an end-to-end data management and annotation platform that integrates seamlessly into ML workflows. It is designed for scalable and efficient dataset curation.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images, videos, and 3D data.
- Annotation Features: Offers tools for semantic segmentation, keypoint annotations, and instance segmentation.
- AI-Assistance: Includes pre-labeling and real-time validation tools.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Fully integrates with platforms like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Scalability and Performance: Handles high-throughput annotation tasks for large datasets.
Collaboration: Robust collaborative tools with role-based task assignments and real-time updates.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: High scalability, extensive feature set.
- Cons: Learning curve for new users.
Export Formats: JSON, CSV, and proprietary formats.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on usage and features.
Use Cases: Perfect for e-commerce, autonomous vehicles, and geospatial analysis.
13. RectLabel

Description:
RectLabel is a tool for annotating images and videos with bounding boxes and polygons for machine learning applications, especially in computer vision tasks like object detection.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Focused on images and videos, primarily for object detection and segmentation tasks.
- Annotation Features: Provides tools for drawing bounding boxes, polygons, and more for precise annotations.
- AI-Assistance: No AI-powered tools; manual annotation only.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Exports annotations in formats compatible with TensorFlow, PyTorch, and other popular frameworks.
- Scalability and Performance: Suitable for small to medium-sized projects but can be used for larger datasets with manual effort.
- Collaboration: Does not support real-time team collaboration.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Simple, easy-to-use interface for object detection tasks.
- Cons: Limited to bounding box and polygon annotations, no AI-assisted features.
Export Formats:
Pascal VOC, YOLO, and others.
Pricing:
Starting price: $19.99 (one-time purchase).
Use Cases:
Ideal for smaller projects or teams working on object detection and image segmentation tasks.
14. Annotorious

Description: Annotorious is an open-source web-based annotation tool that simplifies image and video labeling for computer vision projects. It provides a flexible and easy-to-use interface.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Focused on image annotation, supporting bounding boxes, polygons, and keypoints.
- Annotation Features: User-friendly interface with easy tools for creating annotations on images and videos.
- AI-Assistance: No AI assistance; purely manual annotation.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Can export data in formats like COCO, which is compatible with popular ML frameworks.
- Scalability and Performance: Suitable for small to medium-scale annotation tasks.
- Collaboration: Basic collaboration features for sharing annotated images.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Open-source, simple to use, lightweight.
- Cons: Limited advanced features, lacks scalability for large datasets.
Export Formats:
COCO, Pascal VOC, and others.
Pricing:
Starting price: Free (open-source).
Use Cases:
Ideal for small projects or individual users working on simple image annotation tasks.
15. Diffgram

Description: Diffgram is an open-source data labeling tool designed for machine learning teams. It supports a wide range of data types and allows for both manual and automated annotation.
Key Features:
- Data Type and Complexity: Supports images, videos, 3D point clouds, and text data annotation.
- Annotation Features: Includes tools for object detection, semantic segmentation, and other tasks.
- AI-Assistance: Provides semi-automatic annotation and active learning capabilities to speed up workflows.
- Integration with ML Pipelines: Integrates with machine learning pipelines and various popular ML frameworks.
- Scalability and Performance: Highly scalable, suitable for enterprise-level projects.
- Collaboration: Strong team collaboration tools with workflow management features.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Open-source, supports various data types, scalable.
- Cons: Some advanced features require technical setup, not as beginner-friendly.
Export Formats:
COCO, YOLO, and more.
Pricing:
Starting price: Free (open-source), with paid plans for enterprise features.
Use Cases:
Best for teams or enterprises requiring scalable, customizable annotation tools for complex data types.
Summary
Selecting the right annotation tool depends on your project's scale, data type, and budget. CVAT stands out for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, while tools like V7 and SuperAnnotate excel in automation and enterprise features. Ensure to match your project needs with the tool’s capabilities to maximize efficiency and quality.
FAQs
What is an annotation tool? Annotation tools are software platforms that enable labeling of data, such as images or text, to train machine learning models.
What factors should I consider when choosing an annotation tool? Key factors include data type compatibility, automation features, collaboration tools, export formats, and budget.
Are there free annotation tools? Yes, tools like CVAT and Label Studio are free and open-source, making them ideal for small-scale or individual projects.
Can annotation tools integrate with ML pipelines? Most modern annotation tools, including V7, Labelbox, and CVAT, offer integrations with popular ML frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch.